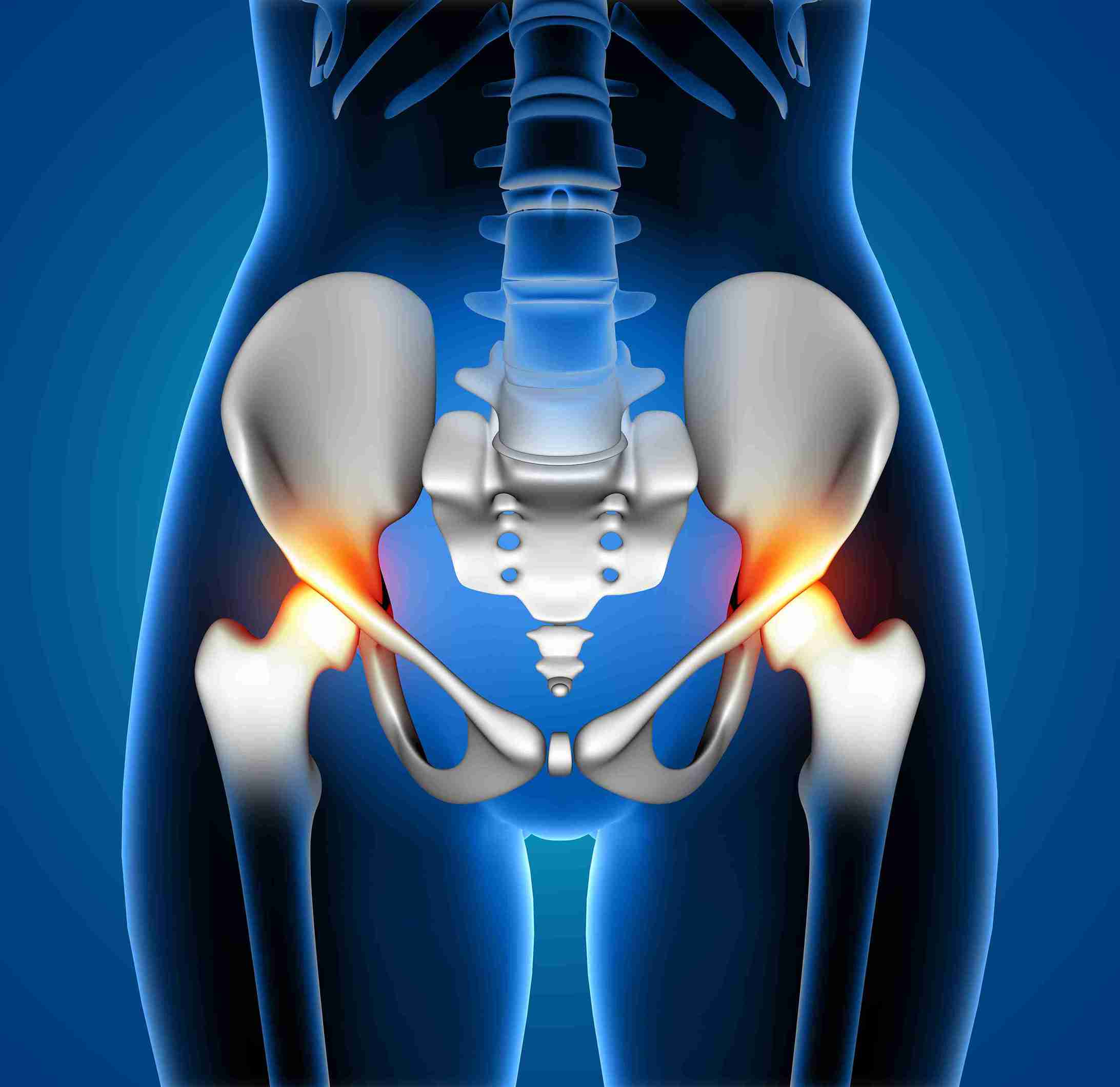
Trochanteric Bursitis is the most prevalent form of hip pain. It occurs due to inflammation of one of the small fluid-filled sacs called the bursa, located near the hip joint. The bursa minimizes friction between tissues in the hip region, but it leads to pain when inflamed. This condition commonly affects runners, cyclists, and people with overuse syndromes.
If you experience joint diseases such as chronic kidney disease or rheumatoid arthritis, you’re more likely to develop trochanteric bursitis.
Signs & Symptoms
Trochanteric bursitis is marked by pain on the lateral aspect of the hip. Symptoms include:
- Tenderness in the hip
- Pain while lying on the affected side
- Increased pain while walking or climbing stairs
- Pain when pressure is applied to the hip
These symptoms interfere with daily activities and resemble multiple myeloma, a disease affecting bones and joints. Consulting a doctor is advised if hip pain radiates to the leg or back.
Etiology
There are several causes:
- Repetitive stress: Running or prolonged standing irritates the bursa, similar to how Runner’s Knee develops.
- Hip injury: Trauma such as a fall can cause bursitis.
- Poor posture: Physical activities with improper posture exert pressure on the bursa.
- Arthritis: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or using tobacco can increase the risk of bursitis.
Though bladder calculi and soft tissue sarcoma do not directly cause bursitis, they may predispose you to joint issues.
Diagnosis of Trochanteric Bursitis
There are no specific tests for diagnosing bursitis. The diagnosis is based on symptoms and clinical examination. Imaging techniques like X-rays or MRIs are used to rule out fractures or arthritis. It’s important not to let these symptoms progress, as with conditions like Kaposi Sarcoma or Bechet’s Disease.
Management of Trochanteric Bursitis
- Rest & Activity Modification: Avoid activities that strain the hip, such as jogging. Consider lower-impact exercises like swimming. Rest is also crucial for conditions like disc herniation.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes multiple times a day to reduce swelling and pain.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen may help. Consult a doctor if you have conditions like high cholesterol or are on long-term therapy.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist may recommend exercises that strengthen the hip and improve flexibility, similar to rehabilitation for femur fractures.
- Steroid Injections: For severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be used but should be done sparingly.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove the bursa, much like the approach in total joint arthroplasty.
Preventing Trochanteric Bursitis
Preventing hip bursitis involves:
- Warm-up exercises: Always stretch before workouts.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: excess weight adds pressure to the hips.
- Wearing supportive footwear: Proper shoes prevent unnecessary strain on the hips and lower back.
- Strengthening core muscles: Yoga and other core exercises help prevent bursitis and maintain balance. Following practices similar to time management for good posture helps alleviate pressure on the bursa.
FAQs on Trochanteric Bursitis
- What treatments are effective for trochanteric bursitis?
Rest, ice application, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, corticosteroids or surgery. - How long does recovery take?
Most people recover within weeks, but chronic cases may take longer. - Does walking worsen bursitis?
Walking on uneven surfaces or for long periods can aggravate the condition, much like overuse in runner’s knee. - Does weight affect trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, excess weight increases hip pressure, worsening the condition. Consider dietary adjustments like a cholesterol-lowering diet. - Is it safe to sleep on the affected side?
It’s better to avoid sleeping on the affected side. Use a pillow between your legs to reduce strain. - Are corticosteroid injections effective?
Yes, but they should be used cautiously, particularly if you have underlying conditions like chronic kidney disease. - What are the complications of untreated bursitis?
Untreated bursitis can become chronic, much like pancreatitis, and lead to persistent pain. - How can I prevent trochanteric bursitis?
Regular exercises and maintaining flexibility help prevent bursitis. Consider yoga for core strength, similar to exercises for back and biceps. - What activities should I avoid with bursitis?
Avoid high-impact activities like jogging or cycling. Incorporate more gentle activities into your routine. - Does physical therapy help?
Yes, physical therapy improves hip mobility and reduces inflammation. Similar treatments are used in managing femur fractures.