Read about Total Knee Replacement
What is Disc Herniation?
Disc herniation is the bulging of the nucleus of a spinal disc through a tear in the annular fibers. This may recover and cause inflammation that affects nerves resulting in pain, numbness or weakness in an arm or leg. Humans have a collection of bones known as vertebrae that make up our spine. Between the vertebrae there are so called intervertebral discs that are semi-rigid and act as shock absorbers. These discs provide cushion to our spine and enables it to flex. Incidentally, if one of these discs herniates, it can greatly trigger certain problems.
Causes of Disc Herniation
Aging: Over time, discs tend to lose water content forming the basis of discos. This makes it less flexible than the other corresponding material, and highly susceptible to tearing. The processes are generally referred to as disc degeneration. With time, there is a reduction of water content in the discs as people age. This drying out makes the discs to become very brittle and prone to cracks or tears.
Injury: A disc can herniate due to efforts to lift a very heavy object or when twisting the back in some way. This arises from cases of lifting an object with the back in a wrong manner or suddenly twisting the body. This could lead to its displacement through a disc this could in turn lead to displacement by another disc.
Repetitive Strain: Poor posture for long periods or repeated movements would over time cause the wearing down of the discs. Any line of work where one bends of lifts, can result to disc herniation and hence should seek professional medical advice. Sitting for long time also has bad effects of body posture that could lead to this ailment as well.
Genetics: People will inherit some disc herniation conditions from their parents and other relatives as a result of their genes. For whatever reason, if members of your family often have disc problems, chances are you could be a candidate for these complications too.
Obesity: Obesity is also known to place a lot of pressure to the discs situated in your lumbar region. This increased pressure can lead to herniation 28 exceptionality The growth of this condition has been observed in the United Kingdom as noteworthy in exceptionality.
Smoking: Smoking can reduce the oxygen supply to the disc tissues, which can lead to more rapid degeneration.
Symptoms of Disc Herniation
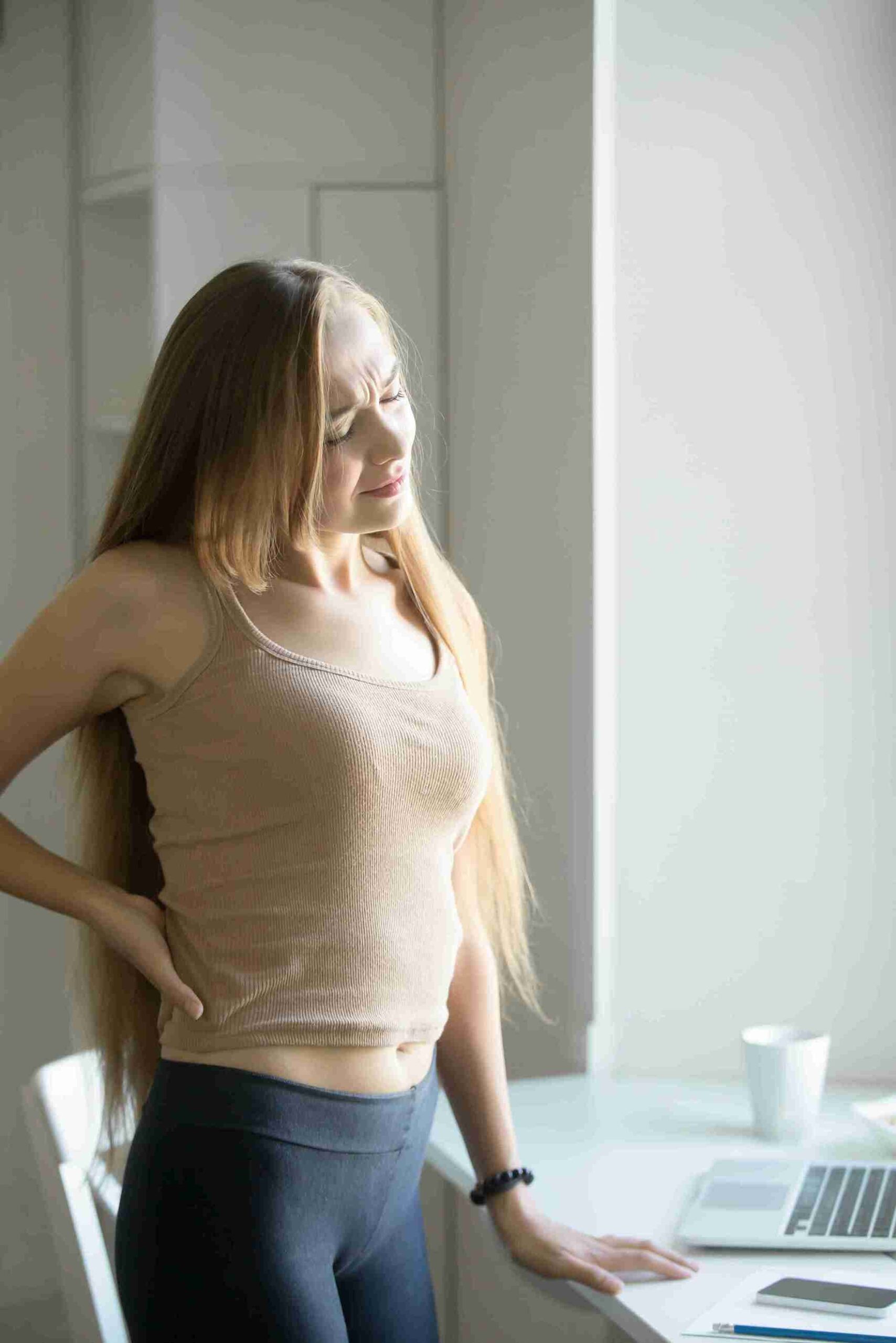
Pain: Numbness, tingling, or loss of feeling in the back, neck, arms and/or legs. The pain may also spread to the extremities of the body particularly the limbs more commonly the legs and the arms. If the herniated disc is in your lower back, the greater pain will be pointed to your buttocks, thigh, and calf muscle. It may also develop in a portion of the foot. If a herniated disc is in the neck, the pain will severely be felt in the shoulder and the arm than in the neck. This pain might radiate into the arm or leg when one is coughing, sneezing, or turn the spine to different angles.
Numbness or Tingling: Tingling sensation in the affected part of the body and/or numbness. Common symptoms of a herniated disc include weakness or even numbness or pins and needles in the part of the body supplied by the nerves.
Weakness: Tenderness and weakness in muscles – especially if the area of pain is the concern. Such muscles pull, tendons and muscles that are supplied with the affected nerve tend to degenerate. This may lead to tripping or a disability to pick or hold objects.
Diagnosis
Physical Exam: Looking for symptoms of neuropathy in a patient. A physical examination involves palpation in which the doctor examines your back and checks whether it is tender. They may also assess especially the speed of your reflexes, your muscle power, the way you walk, response to light touch, pin prick, or vibration.
Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to get better access to the condition of the spine. All these tests can demonstrate the position and extent of the herniated disc and the involved nerves.
Nerve Tests: Electrocardiogram (ECG) for diagnosing heart disease. These tests help determine the ability of your nerves to transmit electricity through them.
Treatment Options for Disc Herniation
Rest and Activity Modification: The client should also avoid activities that cause an exacerbation of the symptoms. Rest is very essential for the health of pregnant women but this does not mean that one has to confine her to bed. However, attempt to move around as much as you can without aggravating the pain even more.
Physical Therapy: Stretches and workouts for the back that aims at help increasing muscular strength on the back area and the flexibility. A physical therapist can educate a person of various exercises which can help a person in increasing the flexibility of the muscles and strengthening the muscles of the back.
Medications: Analgesics, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and Musculoskeletal relaxants. A person should take an anti-inflammatory drug over the counter that includes ibuprofen or an acetaminophen that can help in addressing pain. At some point, your doctor could recommend that you have stronger pain controlling medicines.
Injections: A daily candesartan therapy and cortisone injections to minimize inflammation. If oral medicines to reduce pain are not effective, your doctor may prescribe a cortisone injection to the region around the spinal nerves.
Surgery: In more serious circumstances especially if the pressure on the nerve is exerted, one may undergo surgery to remove or fix the herniated disc. Surgery should be an absolute last resort and is usually only attempted after six weeks of trying other forms of primary treatment. Your doctor may surgically take out the part of the disc that causes the bump, or in an uncommon case, eliminate the whole disc. Sometimes, a surgeon may fix the vertebrae with a metal graft to boost the spine’s stability in the body.
Preventing Disc Herniation
Exercise Regularly: Have a good back to be strong and flexible. Fifty minutes of exercise is recommended in week for the muscles that surround the spine to be strengthened consistently. Concentrate on the activities that involve the muscles of the abdomen and back.
Maintain Good Posture: Take a seat and get up appropriately. Proper position relieves the stress that may be exerted to your backbone and discs. Ensure that you work on ergonomically designed furniture and do not slouch.
Lift Correctly: To move items which are heavy, ensure you use the legs, not the back. Maintain your back free, meaning that you should not bend your back while bending your legs. Keep the object in contact with your skin.
Stay Hydrated: One should take much water in order to maintain the proper hydropathy of discs. The other benefit of ensuring that your body is well hydrated is that it supports the state of the discs thereby making them more elastic and slippery.
Healthy Weight: This implies that Obesity exert pressure on spine, therefore adopting a healthy lifestyle is an effective way of decreasing it. Obesity also takes extra pressure on the disc in the lower back resulting to disc hernia.
Living with Disc Herniation
Stay Active: Pain can be eased through exercising but this should be done at cool and gentle intensity. Daily exercises involving little motion such as walking swimming or yoga are also encouraged. Do not carry out exercises that can cause movements on the spinal column, activities that make your spine vibrate.
Use Supportive Furniture: Comfy chairs that will address the lower back. Organize your working environment in a way that is most ergonomic. Sit on a chair that the lordotic curve of your spine should comfortably rest on.
Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Ensure you use a firm mattress and the sleeping positions that help in maintaining the spinal alignment. Raising the head and legs 15-20 cm with a pillow under knees also can be useful also. Laying on your back, position a cushion beneath your legs if you are a back sleeper.
Disc herniation is thus a fairly widespread problem, which, however, can be effectively treated. Knowledge about the cause, signs/aches, and management of the condition will enable one to live a pain-free existence. Any problems with a herniated disc should be taken to a doctor as soon as possible. This shows that if the condition is treated early, any further complications can be avoided.
So, it is possible to control the disc herniation following these recommendations. Be sure to remain active for your back and experience lesser back pains. Do not forget that the spine management is a long-term process in which everyone is involved. If you keep the correct lifestyle habits then you can lower your susceptibility to disc herniation and have a healthy strong back in the foreseeable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a disc herniation?
A disc herniation occurs when the jelly like center of the spinal disc gets out through a tear in the outer fibrous ring, overloading nearby nerves. This condition can results in pain, numbness, or weakness in the areas where they are injected.
What causes disc herniation?
The common risks factors include age, injury, repeated stress, heredity, being overweight, and smoking. Such aspects lead to the deterioration of spinal discs thus causing the disc to herniate.
What are the common symptoms of disc herniation?
Some of the signs and manifestations of radiculitis are pain in the back, neck, arms or legs, paresthesia, that is, numbness, and sensations of tingling, and perhaps muscle weakness. The manifestation is quite diverse, and it is characteristic that its specific form depends on the zone of the herniated disc.
How is disc herniation diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests used in the diagnosis of disc herniation include physical examination, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) scan and Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) or electromyography (EMG). These methods assist in pinning down the precise location and extent of the herniated tissue.
What are the treatment options for disc herniation?
The mode of managing the condition include using anti-inflammatory drugs, promoting rest, using injections and in some recessed cases using surgery and physical therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the degree of manifestations and the individual characteristics of the patient’s condition.
Can disc herniation be prevented?
Indeed, disc herniation can be averted through physical exercises, correct lifting of the objects, adequate water intake, proper weight, and cessation of smoking. These practices contribute to spine health and the prevention of this condition such as herniation.
Is surgery always necessary for disc herniation?
Disc herniation does not always require a surgery. Many situations can be addressed with non-surgical treatments, for instance, exercises, medicines and modifying one’s lifestyle. Surgery is only used if all these methods do not work out in a patient and the symptoms persist.
How long does it take to recover from a herniated disc?
Healing time differs with the extent of the herniation and the approach that he or she offers to fix the problem. Depending on the kind of conservative treatment that is administrated, most individuals begin to experience an alleviation of symptoms within several weeks. Complete rehabilitation can take several months, more so if one includes surgery on the joints.
Can exercise help with disc herniation?
Yes, exercise can help for disc herniation. Walking, swimming, or practicing yoga are some of the mild activities that can help to build up the muscles that surround the backbone, flexibility in the feminine and decrease the pains. Especially, one should not overexert himself or herself and adhere to recommendations provided by a physical therapist to prevent potential harm.
What lifestyle changes can help manage disc herniation?
Disc herniation can be managed by changing some of the lifestyles like; exercising, using proper appropriate furniture, sleeping well and exercising, and achieving a healthy body weight. These changes benefit spinal health and may help the extent and occurrence of the symptoms as well.












