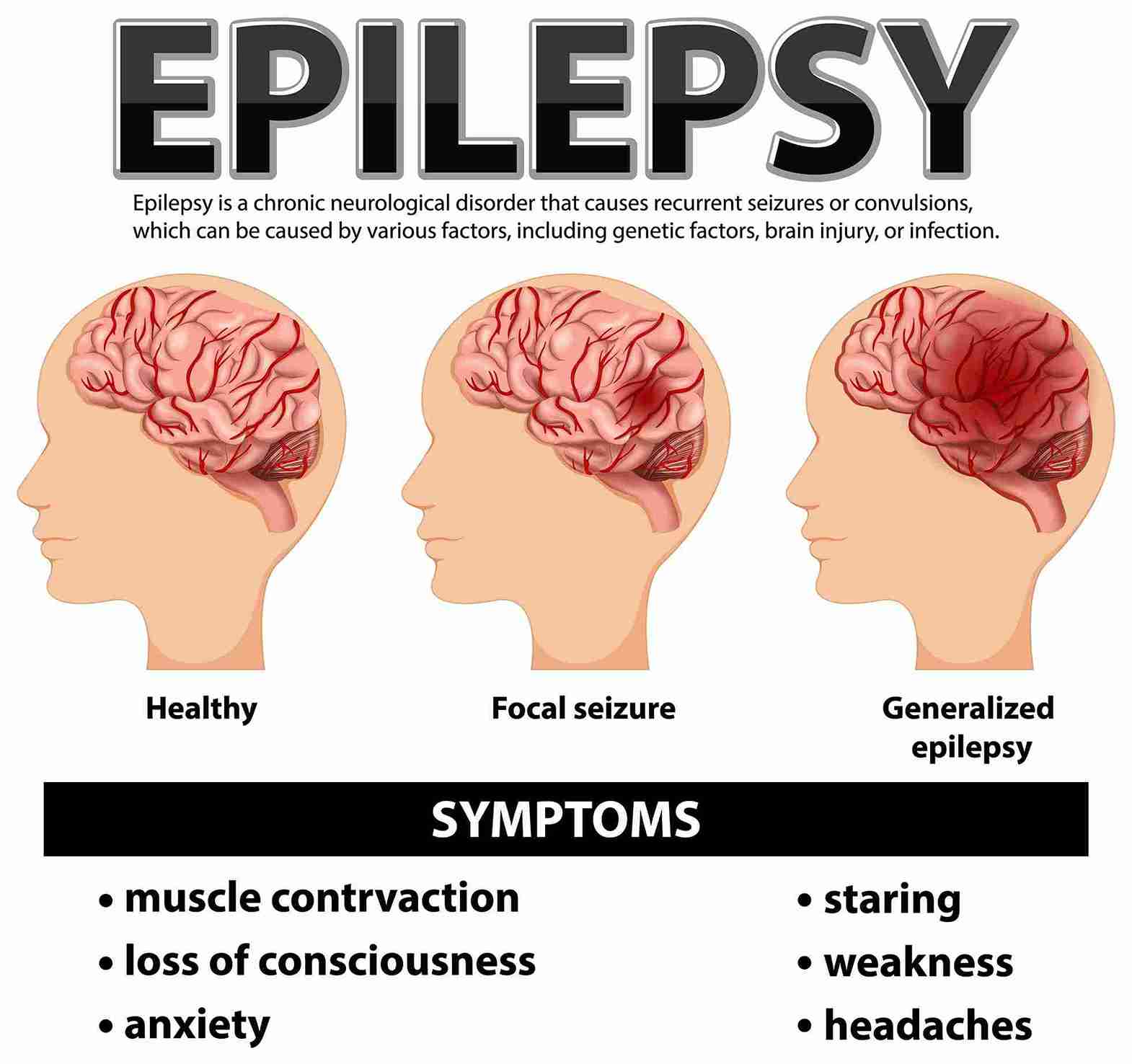
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is one of the diseases that affects the brain and which has no known cure. This is determined by the ability of the patient to have repeat cases of seizures. These seizures are incidents of irregular electrical work of the brain. Epilepsy does not mean one illness but actually it is a category of many abnormalities with the similar symptoms and the different treatment. However, it must be stressed that having one seizure does not mean that the person has epilepsy. Epilepsy is a condition, where a person has at least two episodes which are unprovoked at different times.
Types of Epilepsy
Epilepsy is categorized based on the types of seizures and the part of the brain affected. Understanding the different types helps in choosing the right treatment.
Generalized Epilepsy
Generalized epilepsy is being characterized by seizures when both the sides of the brain are involved from the beginning. These seizures might lead to fainting and also the contraction of muscles in the body in a violent manner. They include such as absence seizures which are episodes of loss of consciousness for a short time and tonic-clonic seizures which are convulsions.
Focal Epilepsy
Focal epilepsy is epilepsy characterized by epileptic seizures having their origin in a part of the brain. These seizures may generalize to other area of the brain. They include odd sensations as well as feelings and movements. Focal seizures can be either simple which means they do not impair consciousness or consciousness or complex meaning consciousness is partially or totally impaired.
Idiopathic Epilepsy
On the other hand, idiopathic epilepsy is defined as that which has no known cause. It is mostly a childhood or adolescent disorder and could well be hereditary. The actual cause of postpartum epilepsy is still unknown, but like most other sorts of epilepsy, it tends to be fairly easy to control.
Symptomatic Epilepsy
Secondary epilepsy is characterized by epilepsy symptoms which are as a result of a known condition, this may be a head injury, a stroke or the result of an infection among others. This category of epilepsy could be more difficult to manage. The primary pathology needs treatment along with the seizures.
Common Symptoms of Epilepsy
The episodes related with epilepsy may be different, depending on the kinds of fits that a person suffers from. Common symptoms include:
Sudden jerking movements: This can be applicable on the arms, legs or the whole body at times.
Loss of consciousness: So, there are some types of seizures which imply the loss of consciousness or, at least, their respondent.
Staring spells: For some kinds of seizures, a person may appear to look as if they are gazing into space.
Confusion: There might be a period of postictal confusion, in which the person is confused; for example, after a seizure, they do not know where they are.
Uncontrollable muscle movements: This includes, shakings or twitching of muscles.
Sudden fear or anxiety: It is common and normal to feel scared or at least a little anxious before or during a seizure for some people.
It is, therefore, crucial to have sufficient knowledge on these symptoms with a view of diagnosing the condition at its infancy. Seizures do interfere with a person’s everyday functioning, so if these signs are noticed one should consult a healthcare provider.
Causes of Epilepsy
Epilepsy can have many different causes. In some cases, the cause is clear, while in others, it remains unknown. The most common causes include:
Genetic Factors
It is, nevertheless, significant to note that epilepsy occasionally can be hereditary. The following genes have been found to be associated with epilepsy; Many types of epilepsy are related to some inherited diseases.
Brain Injuries
There are causes of epilepsy, for example, head injury in an auto accident or fall and other related causes. Studies revealed that whether epilepsy will appear depends on the injury’s severity and location.
Infections
Causes of epilepsy include brain infections including meningitis or encephalitis that could make a section in the brain inflamed. These infections can affect the brain and cause conditions under which a person could experience a seizure.
Stroke
Epilepsy has present association with stroke, and this is largely resonated in the elderly population. A stroke is an event that takes place when the circulation of blood in the brain is affected leading to damage of the organ. This damage can cause seizures and in the long run can cause epilepsy.
Developmental Disorders
It is worth mentioning that such diseases as autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and neurodevelopmental delays increase the probability of epilepsy development. Although the relationship of these conditions to epilepsy is still not well explained it is believed that abnormal development of the brain is to blame.
How is Epilepsy Diagnosed?
Medical History
In diagnosing epilepsy it starts with the taking of a history of the patient’s health. The doctor will enquire about the patients’ past health, their family history or any occurrence of seizures. The above information aids in determining the likelihood of the cause or what brings about the seizures.
Neurological Exams
Neurological tests and procedures evaluate the brain and the nervous system’s performance. These tests check the patient’s and his/her ability to recall information, their reflexes, the muscle movements, and the ability to coordinate them. This may be obvious in case of abnormal results since it can point out some sections of the brain that may be leading to seizures.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Epilepsy diagnosis utilizes several degrees of EEG, and it is the most prominent among all diagnostic tests. It documents the electrical output of the brain via electrodes which are positioned on the scalp. Discharge patterns in the x-ray of the head may portray Epilepsy.
Imaging Tests
MRI and other imaging tests help give pictures of the head and therefore help show images of the brain. It is useful in defining structural lesions, for instance, tumors, that could be determining seizures.
Blood Tests
Serum biochemistry and hematology may be done to investigate the possibility of other causes for the onset of seizures such as infection, electrolyte abnormalities or primary metabolic/genetic disorders.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the right treatment plan. Each patient is unique, and the approach to treatment must be tailored to their specific condition.
Treatment Options for Epilepsy
Epilepsy treatment aims to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures. While some people achieve complete control over their seizures, others may need ongoing treatment. The most common treatment options include:
Medications
Anti-seizure medications are the clam used in treating epilepsy. These drugs act by lowering the chances of having a seizure because they balance the electrical impulses in the brain. Stabilization of the dosage takes some time, and people have to switch through different medications finally choosing the most suitable ones for them.
Surgery
If medication is not effective individuals may opt for surgery. Surgery differs in that a surgeon will have to make a cut in order to take out the portions of the brain that cause seizures. This option is generally opted for when seizures are consistent with an area of the brain and when anti-seizure medication cannot help.
Lifestyle Changes
It is established that there are modifications of the lifestyles that could either positively or negatively affect seizure outcomes. These include getting into a good sleep, taking balanced diets, handling stress well, and avoiding usual conditions that may lead to the occurrence of a seizure for instance light or certain drugs.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Thus, VNS is indicated for patients who have failed the medical management or surgery for epilepsy. Tiny electrode, leads or stimulation generator is sited beneath the skin in the chest and linked to the Vagus nerve in the neck. The device electro-simulates the brain, combating epilepsy at the same time.
Ketogenic Diet
Ketogenic diet is a diet that is high in fats and low in carbohydrate that has been confirmed to minimize seizures particularly in children with this complications. The diet makes the body burn fat and not carbohydrates, and this is thought to have an anti-seizure affect.
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS)
RNS is relatively a new treatment in which a device is inserted in the brain to help the patients. It tracks the electric signals in the brain and applies electrical current to stop the seizure before it happens. This therapy may not be reversible and is typically applied for persons with focal epilepsy who appear to be unresponsive to other therapies.
Neurological conditions like epilepsy can complicate the treatment of other serious diseases such as Kaposi Sarcoma, especially when immune system compromise is involved.
Living with Epilepsy
Living with epilepsy can be challenging, but with the right support and management, many people lead fulfilling lives. Here are some important strategies for living with epilepsy:
Education
Learning about epilepsy is one of the crucial phases of the management of the disorder. It entails the types of seizures, their causes, and the most appropriate treatment should be explained to patients and their families. In decision-making, education ensures that a person makes the right decisions and hence, bypass the feeling of anxiety.
Support Systems
This paper stresses that social relations are important and people with epilepsy should have family and friends that support them. This can involve relations, friends, doctors, and other persons with similar experience form support groups. Telling the story to other patients with epilepsy will in a way empower them and help them to learn from you and your experience.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Epilepsy requires constant check-ups, therefore, it is recommended that people with epilepsy should visit a healthcare provider frequently. These check-ups assist in managing side effects of the new drugs, changing portions of the drugs, and dealing with new ailments.
Safety Precautions
The safety of the epileptic person is a significant concern usually observed by those around him or her. There are measures that can be observed to avoid the risk of getting injured during a seizure. For instance, do not swim alone, use a helmet when cycling and be cautious when handling tools such as knives or when heating oil.
Seizure Action Plan
The enforcement of a seizure action plan is the way to go. This should also contain measures that can be done toward and after a seizure, number of people who should be notified in case of an emergency, and instructions for the caregivers.
Epilepsy in Children
Children are not just miniature adults and epilepsy in children is different from that in adults. Any fits can hamper the development, progression in learning process and organizational behavioral pattern of a child. Hence, parents and caregivers should consult or cooperate with the health care practitioners in order to get the best outcome for the child.
Understanding Seizure Triggers in Children
Potential precipitating factors of seizures in children are stress, sleep deprivation, use of certain medication. Such causes should be avoided in as much as possible so as to minimize the chances of the seizing episode. Moreover, parents also should be concerned with the child’s academic performance in school and share with teachers his/her state.
Treatment Options for Children
Candidature with epilepsy can be made to take anti-seizure medications; dietary therapy or even surgery in the worst cases. As for the choice of treatment, it is made depending on the type of epilepsy and the state of the child’s health.
Support for Families
This paper focuses on the sources of stress on parents when they have a child with epilepsy. One can deduce that such support groups and counseling can be of great assist to families. It is recommended that parents who have children with epilepsy get into touch with other parents who have children who also have epilepsy because it will give them a social support group and else a lot of advice.
Epilepsy and Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special time, and women with epilepsy require additional care to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery. With proper management, most women with epilepsy can have a successful pregnancy.
Planning for Pregnancy
It is requested to pregnant women with epilepsy, they should seek advice from the doctor before getting pregnant. Certain anti-seizure medicines can harm the developing fetus and some preparations may be required before conception.
Managing Epilepsy During Pregnancy
The monitoring of epilepsy condition should be undertaken frequently during a pregnancy. Epilepsy control in pregnancy is significant for the mother and baby’s health. It is recommended that a pregnant woman adheres to her doctor’s advice as regards the intake of drugs, foods, and activities.
Breastfeeding and Epilepsy
Women with epilepsy should consult a healthcare provider about breastfeeding as it is generally safe for most women with epilepsy. Certain drugs are known to be excreted in breast milk; therefore, certain changes may have to be made.
Postpartum Care
After childbirth, women with epilepsy may experience changes in seizure frequency. Continued monitoring and support are essential during the postpartum period.
Conclusion
Epilepsy is a very general and relatively poorly understood disease, but when treated properly most patients with epilepsy can live normal functioning lives. It is therefore an important feature for one to know with precision the causes, symptoms, and possible treatments of epilepsy. On this guide, one is able to get the basic information about epilepsy whether you are a patient, a personal caregiver or anyone with interest in the illness. It is advisable to seek the services of a doctor when having any health issues, regarding a given issue.
FAQ’s
What is epilepsy?
Epilepsy is defined as a neurological disorder that affects a patient through instabilities in the electric activity within the brain which lead to reoccurrence of seizures.
What are the common symptoms of epilepsy?
Some of the signs that one can observe include sudden and abrupt shocks, loss of orientation, conditions that give a blank look, twitching of muscles, and even convulsions.
What causes epilepsy?
Epilepsy is clearly influenced by hereditary factors; head injuries; infection; strokes; and developmental problems. Sometimes the exact cause is not known, but more often the cause of such feelings is easily discerned given the circumstances surrounding the deceased.
How is epilepsy diagnosed?
The cause is determined medically through history taking, neurological assessments, EEG, imaging, and seldom, blood tests.
What are the treatment options for epilepsy?
The following is the possible approach, including the medical one: anti-seizure medications, surgery, changes in life habits, VNS, ketogenic diet, RNS.
Can epilepsy be cured?
Epilepsy is a disease that cannot be cured but there are many ways a person can minimize seizures and live a normal lifestyle.
Is epilepsy hereditary?
Certain types of epilepsy are hereditary and as such may be passed down from one generation to another but this is not all forms of epilepsy.
Can people with epilepsy lead normal lives?
Absolutely, the victims of this disease can live normally fulfilling lives as soon as they receive treatment and medical assistance.
What should I do if someone has a seizure?
Do not panic, ensure the individuals safety, do not contain the person and measure the seizure. In case it it goes beyond five minutes, the person is advised to call an ambulance.
Can epilepsy affect pregnancy?
This means that women who have epilepsy should not worry about giving birth to a child since they can do that successfully as any other women if they consult their doctors and adhere to the recommended measures during pregnancy. Basically, patients should have a possibility to cooperate with healthcare providers.