Respiratory Acidosis vs Alkalosis
Respiratory Acidosis vs. Alkalosis is a crucial aspect of enhancing basic knowledge of the human body. The blood pH is another means maintained with precision by our body. it is constantly checking the proportion of acid and base towards affecting any change. This balance is important for so many body functions like the rate of enzymatic reactions and muscle contractions. In this equilibrium loss due to lung and breathing difficulties, respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis may develop.
pH and Its Role in Avoiding Respiratory Acidosis vs Alkalosis
Each one of us has a specific function and each function is interconnected with the other one. Stability is also paramount, especially when it comes to balancing the variable measured bicarbonate ions and blood pH.
What is pH?
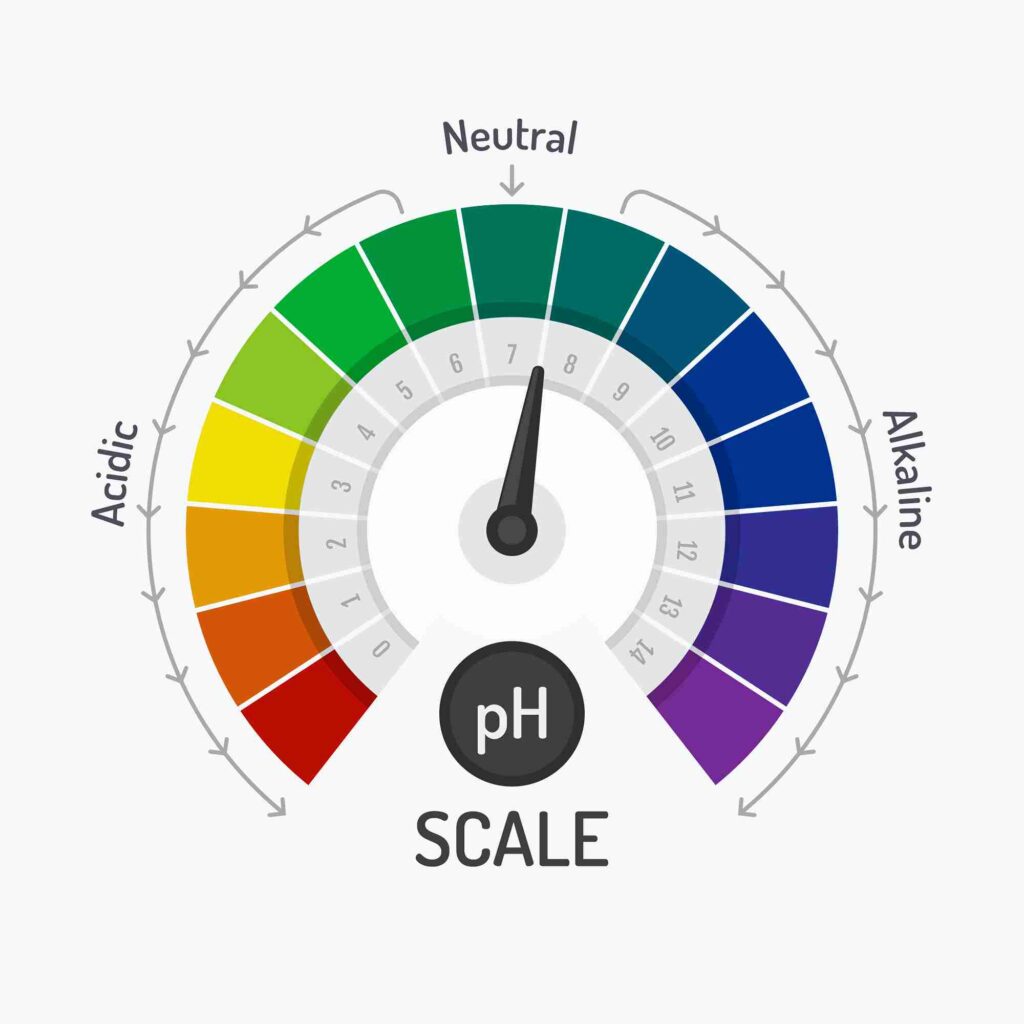
Pretend with a scale from 0 to 14. Zero to 6 are considered acidic and above 7 are considered alkaline or basic solutions for that from 0-6 it is acidic, 7 neutral, and 8-14 it is alkaline. The acid-base balance of blood lies in a specific range, usually between 7. 35 and 7. 45. It is essential for several processes occurring in the human body like the enzymatic activity of certain enzymes that are involved in the digestion of food and muscular contraction, which enables motion.
Acid-base balance is important because body pH determines the permeability of the cell membranes, the rate of metabolism, enzyme activity, and the ability of hormones to cross cell membranes.
Acid/Base Production
Our body is a factory that produces acids and bases all the time through chemical reactions such as digestion and metabolism. But still, a stable pH should be maintained at all times or hugely installed in any newly developed form of water purification system. Scientists estimate that this proper acid’s alkaline ratio gets thrown out of whack if the line shifts slightly toward either side acidosis or alkalosis. Of course, this can lead to a chain of problems that could potentially affect our ability to breathe, our cardiac rhythm, and even our awareness.
The statistics of kids suffering from some chronic diseases are on the rise. our lungs and kidneys switch to the tag of acid-base balance all the time. Respiratory acidosis is caused by impairment in the lung’s ability to expel carbon dioxide, which is an acidic byproduct. In contrast, respiratory alkalosis occurs when one hypoventilates, that is, breathes too much, resulting in low levels of carbon dioxide, and, therefore, an alkaline balance.
Avoiding Respiratory Acidosis vs Alkalosis
Enzyme activity: Enzymes are tiny workers in our body cells and it is highly effective provided that the pH level of the area is correctly set.
Muscle function: Skeletal muscle contractions require adequate adjustment of blood pH within the body allowing for proper contractions.
Lungs are also heavily involved in this bill-balancing theme of the respiratory system. They endeavor to expel carbon dioxide which is a by-product of cellular respiration and has a slightly acidifying tendency. Here’s how respiration helps maintain a healthy blood pH:
Inhale: Oxygen finds its way into our body and is crucial in the various cellular activities within the human body.
Exhale: We breathe out carbon dioxide which is a little more acidic compared to other waste products.
However, imbalances can occur, leading to two conditions: This may lead to respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis.
Respiratory acidosis
Because the body uses the lungs to expel carbon dioxide, when it is unable to do so effectively it results in the blood becoming too acidic. COPD, heart or lung disease, or even sleep apnea can be the cause of this. Even Chronic respiratory acidosis can be a contributing factor to hypertension.
Respiratory alkalosis
This is the case when one hyperventilates, such as during a panic attack, and CO2 is expelled in excess hence reducing the PH of the blood to become less acidic.
Respiratory Acidosis
Just as your lungs filter the air and remove waste products, it may imagine what they would be like within the body. In respiratory acidosis, these filters are overwhelmed, and hence a gradual accumulation of an acidic byproduct called carbon dioxide in the bloodstream. This disturbs the balance already mentioned above:
Causes of Respiratory Acidosis
Several factors can contribute to respiratory acidosis:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): This lung condition affects respiratory function, especially in the removal of carbon dioxide in the human body.
Sleep apnea: The general symptoms of this sleep disorder involve a temporary halt in breathing with subsequent build-up of carbon dioxide.
Drug overdose: Some drugs, if administered in large doses, impair respiration and induce acidosis.
Neuromuscular disorders: In particular, conditions of nerves and muscles can impair the muscles utilized for respiration.
Pyogenic liver abscess: While pyogenic liver abscess itself isn’t a common cause, severe cases can lead to respiratory acidosis.
Symptoms of Respiratory Acidosis
If your body struggles to maintain a healthy blood pH due to respiratory acidosis, you might experience some of these symptoms:
- Confusion
- Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Drowsiness
- Rapid breathing
Management of respiratory acidosis
The treatment of respiratory acidosis depends on the cause of the disorder for specific action to be taken. Here are some general approaches:
Treating the underlying condition: It is important to address what is causing increased sleeping difficulty such as COPD, sleep apnea, or anything else.
Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen causes the blood to take in more oxygen and expel Co2 because it binds to the O2 molecules.
Breathing support: In serious conditions, a patient might require the use of a mechanical ventilator that will assist in his/her breathing.
Respiratory Alkalosis
We’ve addressed respiratory acidosis, a condition in which the lungs are unable to expel enough carbon dioxide. Now let’s flip the coin and look at respiratory alkalosis. This situation arises when we overbreathe, resulting in excessive carbon dioxide removal and a shift to an alkaline blood pH.
Causes of Respiratory Alkalosis.
Several factors can cause respiratory alkalosis.
Anxiety and panic attacks: Rapid breathing might cause excessive carbon dioxide loss.
High altitude sickness: It occurs when there is insufficient oxygen, requiring fast breathing to compensate.
Severe pain: It can cause quick, shallow breathing, resulting in alkalosis.
Salicylate (aspirin) overdose: Taking too much aspirin can disturb the body’s acid-base equilibrium.
High Anion Gap: Respiratory alkalosis can sometimes coexist with a high anion gap, masking the severity of an underlying acid-base disorder.
Symptoms Of Respiratory Alkalosis
While keeping a healthy blood pH is important, being extremely alkaline can potentially cause difficulties. Here are some possible signs of respiratory alkalosis.
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- tingling in the hands and feet.
- Muscle twitching
- Confusion
Treatment Options for Respiratory Alkalosis
The treatment for respiratory alkalosis focuses on fixing the underlying cause and dealing with fast breathing:
Calming tactics: Deep breathing exercises and other relaxation techniques can help slow breathing during anxiety or panic attacks.
Supplemental oxygen: In some circumstances, giving oxygen can help to control breathing patterns.
Treating the underlying issue: If pain or another medical condition is to blame, addressing the fundamental cause is critical.
Fortunately, respiratory alkalosis is typically less severe than acidosis. However, if your symptoms linger or you have difficulty breathing, you should seek medical treatment. Understanding the differences between pulmonary acidosis and alkalosis allows you to maintain a healthy balance and promotes excellent lung function.
Prevention and management tips for respiratory acidosis & alkalosis
Our lungs are crucial organs that help maintain a healthy blood pH and prevent abnormalities such as respiratory acidosis vs. alkalosis. Here are some ways to keep your lungs healthy.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Lungs
Don’t smoke: Smoking harms lung tissue and reduces oxygen exchange.
Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity enhances the respiratory system.
Maintain healthy air quality: Avoid air pollution and irritants wherever possible.
Get vaccinated: To avoid respiratory diseases, keep your vaccines up to date.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
Early identification and treatment are essential for both respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. Here are some signs to look for:
- Persistent shortness of breath
- Having difficulty breathing at rest
- Unusual breathing patterns
- Regular coughing or wheezing
- Chest discomfort.
- Confusion or dizziness.
If you see any of these symptoms, see a doctor. They can evaluate your condition, establish if it is due to respiratory acidosis or alkalosis, and offer suitable treatment.
By practicing healthy habits and seeking medical assistance when necessary, you can keep your lungs healthy and avoid imbalances that might upset your body’s delicate acid-base balance. Remember, a healthy breath equals a vital breath!
Frequently Asked Questions about Respiratory Acidosis vs Alkalosis
1. What’s the distinction between respiratory acidosis and alkalosis?
Both disorders result in blood pH abnormalities produced by lung function. Respiratory acidosis occurs when the lungs are unable to eliminate enough carbon dioxide, causing the blood to become overly acidic. Respiratory alkalosis happens when we overbreathe, eliminating too much carbon dioxide and resulting in an alkaline shift.
2. What symptoms are associated with each condition?
Symptoms of respiratory acidosis include shortness of breath, headache, and confusion. Respiratory alkalosis can result in disorientation, tingling in the hands and feet, and muscular twitching.
3. What are the causes of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis?
COPD, sleep apnea, and drug overdose are all potential causes of respiratory acidosis. Anxiety, high altitude sickness, or an overdose of aspirin can all cause respiratory alkalosis.
4. What are the treatments for these conditions?
The appropriate treatment is determined by the underlying cause. Treatment for respiratory acidosis may include addressing the underlying condition or administering oxygen therapy. Respiratory alkalosis treatment relies on relaxation techniques or addressing the underlying cause, such as pain.
5. How can I avoid respiratory acidosis and alkalosis?
Maintaining healthy lungs is essential. Quit smoking, exercise regularly, and avoid air pollution. Vaccination helps to avoid respiratory diseases, which can lead to these imbalances.
6. When should I visit the doctor?
If you have recurrent shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or strange breathing patterns, see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for both respiratory acidosis and alkalosis.











2 Comments