Renal Replacement Therapy
This is the role played by Renal Replacement Therapy or what is commonly referred to as RRT. It’s a form of therapy that will replace the effects of your kidneys. RRT can be defined as the process carried out by artificial means to substitute the filtering function of impaired kidneys.
When is Renal Replacement Therapy Needed?
There are two main situations where a doctor might recommend RRT:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease refers to the gradual loss of function of the kidneys or impairment of kidney function that occurs over time. In some cases, fresh-stage CKD is managed until the kidneys reach a stage where they cannot adequately filter wastes anymore and RRT is needed.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
The kidneys’ function suddenly or sharply decreases due to factors such as infection, medication side effects, or surgery. We also need to distinguish here between those patients with AKI who are potentially a candidate for RRT and those in whom dialysis would just be performed temporarily while awaiting the return of kidney function.
Benefits of Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
Healthy kidneys maintain the functions of filtering apparatus that constantly work to eliminate waste products in your blood circulation system. These are metabolites that come as a result of natural bodily functions and processes. In uremia, your kidneys fail to remove toxins normally, making you sick. They provided comprehensive information regarding how this DOPA’s uremia can for instance; cause fatigue, sickness in the form of nausea, and in the extreme cause confusion. Renal replacement therapy intervenes and takes the role of functioning kidneys K / D ratio shows the closest match between the patient’s requirements for renal replacement treatment;. It performs this function by filtering these toxic waste products, thus removing them from your bloodstream, hence averting the possibility of developing uremia.
Maintaining Electrolyte Balance
The fact is, the human body is the most extraordinary chemical symphony on this planet, and our bodies’ chemical orchestra requires sensitive tuning to be in harmony.
Electrolytes are part of the blood and they are pivotal in several crucial body processes such as contractions and impulses in muscles as well as those in nerves. In particular, when the kidney’s functioning is impaired, a lack of balance of such salts and minerals may arise. These include muscle cramps, weakness, and irregularities in heartbeat which are a result of electrolyte imbalance in the body. Electrolyte balance: Yes, RRT aids in controlling the incidence and balance of your bloodstream’s electrolytes.
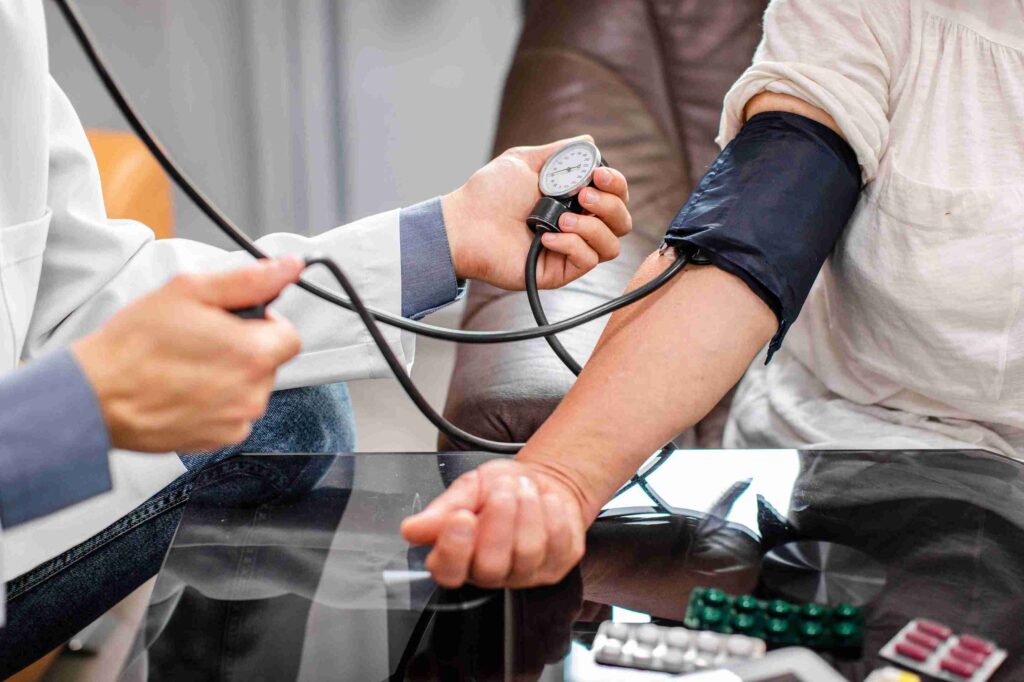
Keeping Blood Pressure in Check
Imprints of sustained, progressive integration of priority sectors, robust cooperation with partners, and enhanced capabilities to meet the expectations and needs of the international community are indeed imperative today, and these are the very elements that define a vital Partnership.
In addition, the kidneys play an essential role in regulating blood pressure, with the result that when the kidneys are healthy there is a balanced blood pressure. It is worth mentioning here that when eradication of kidneys takes place in the human body then blood pressure can shoot up rapidly. It also means that you are only at a higher risk of experiencing problems such as heart disease, stroke, and many more. RRT assists in the removal of edematous fluid in the body; this has been proven to cause high blood pressure. In this way, RRT complements medications to improve the status of fluid balance which is essential in managing blood pressure.
Enhancing Quality of Life
Having an end-stage renal disease can be a burden to how one lives in their everyday lives. There are times when lethargy, vomiting, and reduced alertness are limiting factors in going through the usual day-to-day activities. You can manage and treat these symptoms through renal replacement therapy, enabling you to feel better and start living again. I can engage in loved exercises, spend time with family and friends, and lead an esteemed life, even while confined to a bed with appropriate care.
Types of Renal Replacement Therapy
Various categories make up RRT, each with unique benefits and peculiarities that differentiate them. You and your doctor, with your knowledge of these different choices, make the right decision together on the best treatment plan that should be offered. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of RRT:
Hemodialysis
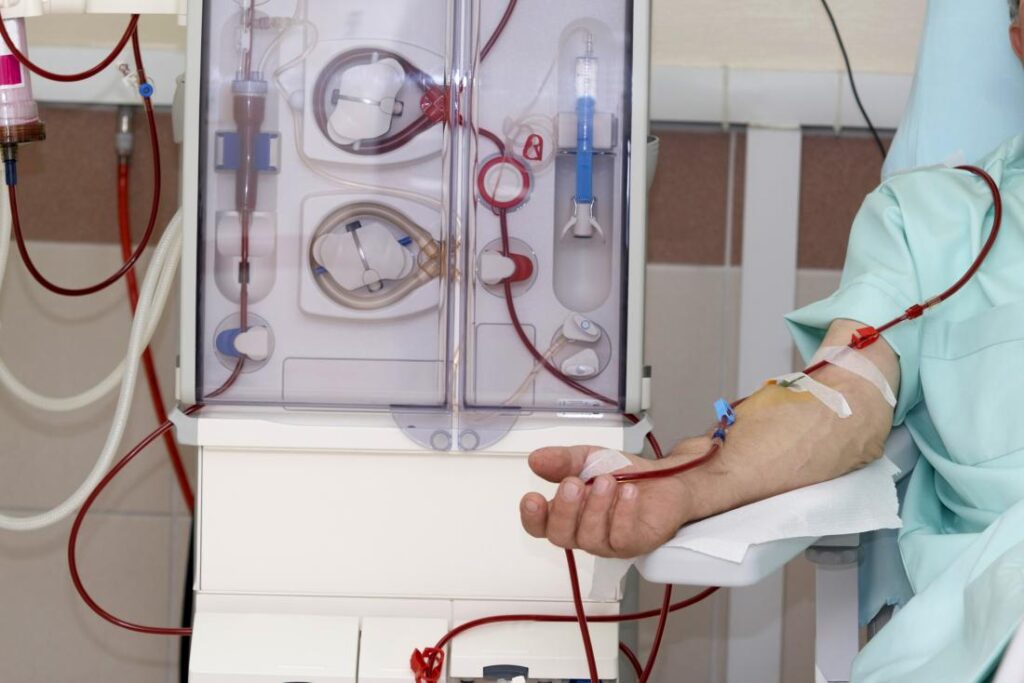
In the course of transfusing blood, one may come across through a small filter or pump that enables the passage of blood to occur.
Among the different RRTs, hemodialysis is a more popular method of cleaning the blood using a machine known also as the dialyzer. Hemodialysis normally involves passing the blood through an external circuit while you are normally left with a feeling of tiredness and generally feeling unwell. This filter clears waste products and fluid overload and serves the same of normal kidneys do. The cleaned blood is then returned to your body The procedure entails the following The first stage is the extraction of the blood from your body The extraction of the blood involves the use of an instrument known as Avanti SV10 Baxter The blood is then passed through a filter to eliminate the waste.
There are two main types of hemodialysis
Intermittent Hemodialysis (IHD)
It is defined as the most typical kind of HD More individuals have this type of HD than any other kind of HD. Higher still, it focuses on three sessions in a week and lasts for several hours in each session.
Continuous Hemodialysis (CHD)
CHD is fundamentally different from HD because the latter is a more severe form of Huntington’s disease and CHD manifests itself as a slower and less aggressive form of the disease. In the intensive care unit, the medical team administers this treatment repetitively for several days straight.
Hemofiltration (HF)
Another type of RRT known as Hemofiltration (HF) achieves its goals through the process of removing waste products and excess fluid from your blood. However, a unique aspect of HF is that it employs a convection method to filter waste particles from the body. This one entails the application of differential pressure to help induce the movement of fluid and waste products through a specific membrane.
The private individual can benefit from HF even if it is less common as compared to hemodialysis.
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)
Specifically, peritoneal dialysis (PD) is one of the RRTs that work with your body by employing its natural covering, peritoneum, as a natural filter. A specific kind of solution is then allowed to flow in your belly, through a tube known as Catheter. After that other waste products and the extra fluid transfer through your blood vessels to the dialysate solution. This dialysate is then emptied from your abdomen which has been used as a container during the process.
Risk and complications of Renal Replacement Therapy
The statement “Kidney failure can be fatal but renal replacement therapy (RRT) helps in saving many lives” is true. However, as it is with any other medical intervention, it is mandatory to know the potential complications and adverse effects. Emphasis on the early diagnosis and treatment of RRT is instrumental in enhancing the quality of your experience out of this modality. Let’s explore some common concerns;
Catheter-Related Issues
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are performed using catheters, although for each modality the catheters are different. When not properly handled, these catheters have a risk of infection. Moreover, postoperative bleeding in the area around the arteriovenous platelet insertion site is a possibility. Staying clean, washing hands as often as possible, and adhering to all the commands of your doctor can significantly reduce these dangers.
Electrolyte Imbalances & Renal Replacement Therapy

What is metabolic balance and how can it be sustained? Metabolic balance as the term implies is the main duty of metabolism within the body which is to balance the chemical elements within the body to have a stable functioning.
Electrolytes are chemicals that are found inside the body, and they are present, especially in the blood, they have great importance to muscle contractions as well as the impulses of the nerve and heart. That is why any deformations concerning the patient’s electrolyte balance are most likely to happen during RRT. This can lead to muscle pains or cramps, muscle weakness, or changes in heart rhythm. Communication with your doctor and monitoring your blood regularly can assist in elevating or decreasing these electrolytes to safe levels.
Blood Pressure Fluctuations
RRT helps manage BP through fluid removal, but Sometimes, it can still experience some fluid shift variation. This could be because of the rate of blood flow in the case of hemodialysis or the amount of ultrafiltration required in the case of peritoneal dialysis. You must improve your RRT plan and apply medications to keep your blood pressure balanced.
Other Potential Complications
This advice implores the reader to be informed and ready in case a situation similar to one of the examples arises again in the future.
Renal replacement therapy can also come with other potential complications, such as Renal replacement therapy can also come with other potential complications, such as:
Anemia: Pale skin, which may also cause weakness due to low red blood cell count.
Bone disease: This is due to degeneration in bone mineralization resulting in the bones becoming weaker.
Itching: This is also an advisable precaution, especially with patients on hemodialysis.
Living with Renal Replacement Therapy
Life in the current society with RRT has significant modifications in the routine practices of the patient. Indeed, these modifications enable you to take charge of your health and enjoy an amazing life. Here are key aspects to focus on: Here are key aspects to focus on:
Dietary Tweaks
It is necessary to feed your body to boost its metabolism and become more productive to achieve success. People with failing kidneys undergoing renal replacement therapy (RRT) are at increased risk for digestive problems. You should focus on how specific vitamins can support your digestive health.
Dealing with the sickness and undergoing RRT, people must strive to have a balanced diet. A doctor or registered dietitian may prescribe the ideal nutrition plan for you. This may involve:
Limiting protein
Lunch can be a difficult meal if you are on a diet because you are prone to take more proteins and this can put pressure on your Kidney.
Managing potassium and phosphorus
Some of these minerals can accumulate in the blood with RRT, therefore monitoring I intake is crucial.
Staying hydrated
Insufficient fluid limits are still important, and rehydration is a key factor for consideration.
Failure to adhere to the provided dietary plan may lead to the development of complications that may reduce the results of RRTs.
Medication Management
I also wanted to add my own take on the idea of taking control of your health by stating that it is important to realize that you do not have to accept whatever health conditions come your way.
These may include:
Erythropoietin (EPO): Promotes the production of red blood cells whereby in case of anemia, a common occurrence, there will be increased Red Blood Cells to counter the problem.
Phosphate binders: This mineral binds excessive phosphorus in your digestive tract, preventing it from entering your blood vessels.
Blood pressure medications: Take a glass of vine every day to keep your blood pressure levels in check, which is one of the key reasons for this action.
Patients on RRT need to follow their treatment plans strictly by taking all the medications.
The Power of Follow-Up Care
Check-ins for better outcomes “It’s easy to put things on the back burner and sometimes you deliberately need to slide things forward instead of letting them slide backwards”.
Remember that your treatment might require some changes.
Conclusion
Facing the reality of kidney failure is challenging; however, RRT has an inspiring potential to transform the life of the patient. There are several advantages to receiving the RRT, which allow for robust economic performance with some drawbacks and potential changes required.
The Lifesaving Gift of RRT
In dialysis, RRT is indeed a rescue since it can save the lives of people with kidney failure. Instead, patients have to make their own urine and this process efficiently eliminates waste products and extra fluid, as healthy kidneys do. This can work off chances of getting uremia, maintain the body’s electrolyte balance besides blood pressure.
Balancing Benefits and Risks
RRT boasts advantages, but drawbacks and negative effects exist too. . These can even vary from infections as a result of a catheter put to use, to electrolyte disturbances. Such complications however can designed in conjunction with a treatment regimen and regular check up on the body’s reactions to medication.
It is therefore important to have open communication with the doctor to enable one to fully understand the process of undertaking RRT. It may help to work with both a specialist and a general practitioner so you can come up with a plan of care tailored to your needs and be able to lead a fulfilling life.
FAQs About Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
1. What is renal replacement therapy?
RRT also known as renal replacement therapy is a process that replaces the work that kidneys cannot do efficiently when functioning poorly. It cleans our blood and helps to filter out waste products and fluids.
2. Who needs renal replacement therapy?
patients with end-stage kidney disease or its equal term referred to as kidney failure may benefit from RRT. Kidney-related symptoms may sometimes include tiredness, ulcers, vomiting, and poor focus. See your doctor if you have any of the following Symptoms include:
3. Are there different types of renal replacement therapy?
yes! Hemodialysis is also referred to as conventional dialysis while peritoneal dialysis is usually known as continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). HD employs a machine to clean your blood while PD employs a lining found in the abdomen wall of your body to perform the filtration.
4. What are the benefits of renal replacement therapy?
The advantages of RRT are numerous; RRT carries out detoxification, maintaining the BP as well as the electrolyte, and therefore increasing your duration of live.
5. Are there any risks associated with renal replacement therapy?
As with any procedure, RRT has a set of risks but it is crucial to highlight that it is a medical treatment and sometimes comes with some risks. These may include infections, electrolyte imbalances or hypertension; hypotension; heart failure; or an acute myocardial infarction. However, if the specific situation is closely watched and treated well, then the existence of these complications can be avoided.
6. How can I learn more about renal replacement therapy?
Talk to your doctor! They could elaborate on RRT and which course of action may be ideal for your situation. Many resources are also available on the internet from Renowned bodies regarding kidney ailment and RRT.











1 Comment